How to apply the Lean Six Sigma method to drive better Customer Experience
ON THE FRONT PAGE OF THIS ARTICLE.
1.Understanding Lean Six Sigma
2. Understanding Lean Six Sigma
3. Applying the method
As part of the Qualtrics XM Institute's Global Study 2023, over 28,000 consumers talked about their recent bad experiences with organizations from over 20 different sectors, and how they reduced their spending with the supplier in question after such an experience.

Poor customer satisfaction is costly
REALLY expensive: 3.700 billion dollars worldwide per year precisely!
How can Lean Six Sigma (LSS) help you?
LSS is a data-driven method for streamlining any type of operation, from a manufacturing line to any company’s customer journey. LSS practitioners will use specific techniques to create a customer-focused organization.
What are the most common factors leading to poor customer service?
LSS is a data-focused method which can streamline any type of operation, ranging from a manufacturing line to the customer journey of any company. LSS practitioners will use specific techniques to create a customer-focused organization.
What is Lean Six Sigma (LSS) exactly?
LSS concepts were first published in a book entitled “Lean Six Sigma: Combining Six Sigma with Lean Speed” by Michael George and Robert Lawrence Jr. published in 2002.
Lean focuses on creating value through the relentless elimination of waste and the acceleration of process speed.
Six Sigma is a voice-of-the-customer management system that strives to deliver near-perfect products or services.
Six Sigma objectives are to reduce defects and variations so that processes are more consistent and perfectly predictable. Six Sigma translates into 99.9997% quality.
Lean Six Sigma implements a genuine culture of continuous improvement through two complementary approaches:
| LEAN | 6 SIGMA |
History | Elaborated at Toyota in the 50’s Came out of Japan beginning of the 60’s Put into theory in the USA in the 90’s | Elaborated at Motorola in the 80’s Developed by General Electric in the 90’s |
Targets for improvement | 0 waste 0 inflexibility | 0 defect 0 variation |
Management methods | Plan Do Check Act (PDCA) Flows optimization | Define Measure Analyze Improve Control (DMAIC) Statistical analysis |
Cultural insights | Staff involvement Standardization | Client voice alignement Permanent (re)targeting |
Common understanding | Culture of operational excellence Research of the creation of real value | |
To make it real, what are the basic metrics to consider?
In any improvement endeavour, the ultimate objective is to make the process:
- Better – DPU (defect per unit), DPMO (defects per million opportunities), variation reduction (less standard deviation)
- Faster – Cycle Time (reduce process time or product development time)
- Cheaper – COPQ (cost of poor quality)
How to apply those methods in the Voice of the Customer governance?
LEAN | Bottom > Up | Top > Down | SIX SIGMA |
Detection of irritants and values Capacity of innovation and improvement Decentralized problem solving to leading operational teams | Definition of Voice of the Customer strategy Translation into operational standards to reach targets of progress Organizational alignment and delegation of responsibilities |
How to combine the best of both worlds?
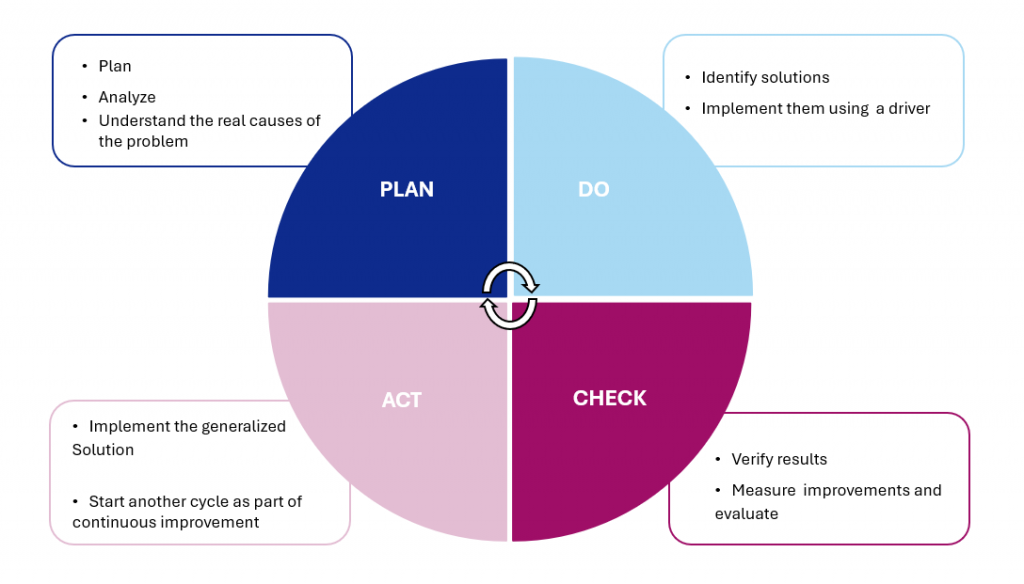
The PDCA project methodology is useful to manage simple actions plan, handling numerous everyday improvements, with a rigorous follow up:
- Plan
- Do
- check
- Act
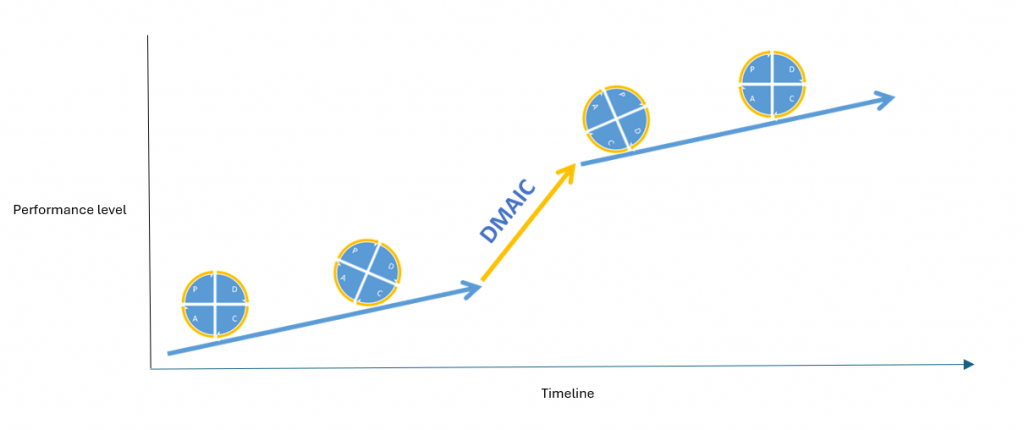
The DMAIC methodology is used to manage complex projects about critical processes, handling only a few disruptive improvements: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control.
What are the success factors for such projects?
- The project must be strongly supported by management, and be the subject of a communication plan at all levels.
- An evaluation based on precise data is necessary before defining a strategy
- Design must be based on business needs, not on the tool itself.
- Dedicated resources (process owner and deployment team) are recommended.
- The measurement system will have to be questioned on an ongoing basis.
- The project should be broken down into manageable lots, but implemented with a long-term vision.
A final word
Applying the Lean Six Sigma method helps you improve each stage of the customer journey. Interaction types and associated channels influence product/service performance and relevance, as well as the quality of customer service.
By reducing process variations and targeting low value-added efforts, this method eradicates sources of irritation for both customers and employees. By eliminating all types of waste, it creates a process focused on the experience of end-users and customers.
Finally, by designing a more efficient and effective organization, it improves value for its customers while reducing costs.
This article is published by:

Yolande Le Mercier
Country Manager at Activeo Swistzerland

